Web Bluetooth

Have you ever wanted to create a web application that enables users to communicate with your device using Bluetooth? Until the introduction of Web Bluetooth, this was only possible through native mobile apps. However, with the advent of Web Bluetooth you can now turn your idea into a reality.
Web Bluetooth is a game-changing technology that allows web developers to connect their applications directly to Bluetooth devices, opening up a wide range of possibilities for IoT, wearables, and other Bluetooth-enabled devices. By leveraging the power of Web Bluetooth, you can create web applications that can communicate with devices without the need for a separate native app.
So if you have been dreaming of creating a web application that can interact with Bluetooth devices, now is the time to explore the possibilities of Web Bluetooth and take your development skills to the next level.
What is Web Bluetooth?
Web Bluetooth is a set of APIs that provide ability to connect and perform actions such as read value, write data, listen to notifications, etc. with BLE peripherals using the Generic Attribute Profile (GATT). This can enable a wide range of use cases, such as controlling IoT devices, syncing fitness data from a smartwatch, or transferring data between a smartphone and a computer.
Web Bluetooth is supported by several major web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Opera, and it also includes a set of industry-standard protocols for secure and efficient communication. However, it is important to note that not all Bluetooth devices may be compatible with Web Bluetooth, as support for the technology varies across different devices and manufacturers.
Upside of Web Bluetooth
- Cross-platform: Web Bluetooth allows developers to create web applications that can communicate with Bluetooth devices on multiple platforms, including desktop and mobile devices.
- Ease of use: Web Bluetooth simplifies the process of connecting to Bluetooth devices, reducing the need for complex native apps or software.
- Accessibility: Web Bluetooth enables web developers to create applications that can communicate with Bluetooth devices without requiring users to install separate apps or plugins.
- Flexibility: Web Bluetooth can be used to connect with a wide range of Bluetooth devices, including IoT devices, wearables, and smart home devices.
Downside of Web Bluetooth
- Browser support: While most modern browsers support Web Bluetooth, some older browsers may not be compatible.
- Security: Web Bluetooth can present security risks if not implemented properly. For example, if an application has access to a user’s Bluetooth device, it may be able to access other sensitive information on the device.
- Limited functionality: Web Bluetooth may not offer the same level of functionality as native Bluetooth apps. This can limit the types of applications that can be developed using the technology.
- Battery life: Bluetooth can be a power-intensive technology, which can drain the battery life of mobile devices. Developers need to be mindful of this when designing applications that rely on Bluetooth connectivity.
Supported APIs
The APIs supported by Web Bluetooth are similar to those available on iOS and Android, which makes it straightforward to work with for developers who are already familiar with Bluetooth technology on mobile devices.
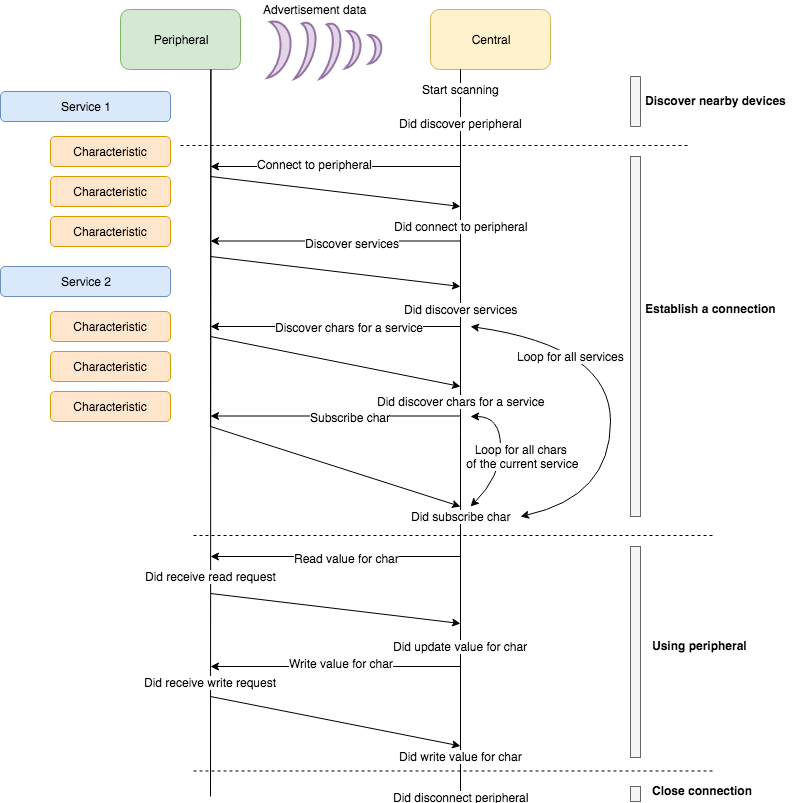
You can review the flow to estashlish a connection to a peripheral at Play Central And Peripheral Roles With CoreBluetooth
navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice(): This API is used to request access to a nearby BLE device. When a user clicks a “Connect” button on your web application, this API is called to scan for available devices and present a dialog box to the user.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24/**
// Discovery options match any devices advertising:
// . The standard heart rate service. OR
// . Service uuid0, and devices with name "ExampleName1", and devices with name starting with "Prefix1" OR
// . Both service uuid1 and uuid2. OR
// . Devices with name "ExampleName2". OR
// . Devices with name starting with "Prefix2". OR
//
// And enables access to the battery service if devices
// include it, even if devices do not advertise that service.
**/
const device = await navigator.bluetooth.requestDevice({
acceptAllDevices: true,
filters: [
{ services: ["heart_rate"] },
{ services: [uuid0], name: "ExampleName1", namePrefix: "Prefix1" },
{ services: [uuid1, uuid2] },
{ name: "ExampleName2" },
{ namePrefix: "Prefix2" }
],
optionalServices: [
"battery_service",
],
});BluetoothDevice.gatt.connect(): This API is used to establish a connection with the GATT server on the selected BLE device. Once a connection is established, your web application can interact with the device’s services and characteristics.1
const server = await device.gatt.connect();
BluetoothDevice.gatt.disconnect(): This API is used to disconnect from the BLE device once the interaction is completed.1
const server = await device.gatt.disconnect();
Get services & characteristics:
BluetoothDevice.gatt.getPrimaryService(serviceUuid): This API is used to retrieve a primary service from the GATT server on the selected BLE device.BluetoothRemoteGATTService.getCharacteristic(characteristicUuid): This API is used to retrieve a specific characteristic from a service.1
2
3
4
5const services = await server.getPrimaryServices();
services.forEach(async (e) => {
const chars = await e.getCharacteristics();
// Doing your logic
});Read & write value:
BluetoothRemoteGATTCharacteristic.readValue(): This API is used to read the value of a characteristic.BluetoothRemoteGATTCharacteristic.writeValue(value): This API is used to write a value to a characteristic.1
2
3
4await char.writeValue(
fromHexString(value)
);
await char.readValue();Listen to
disconnectedevent: This event listener is triggered when the device disconnects from the GATT server.1
2
3device.addEventListener('gattserverdisconnected', () => {
// Your callback
});Listen to value changed: This event listener is triggered when the value of a characteristic changes. This can be used to receive real-time updates from the device.
1
2
3device.addEventListener('characteristicvaluechanged', () => {
// Your callback
});Listen to notification
1
2await char.stopNotifications();
await char.startNotifications();
A simple example
At Web Bluetooth example, I have created a simple website that showcases a set of APIs. This demo website provides developers with an easy-to-use interface for testing and understanding the functionality of the APIs. By accessing this demo website, developers can quickly gain insights into how the APIs can be integrated into their applications.
By default, the web scan all nearby devices.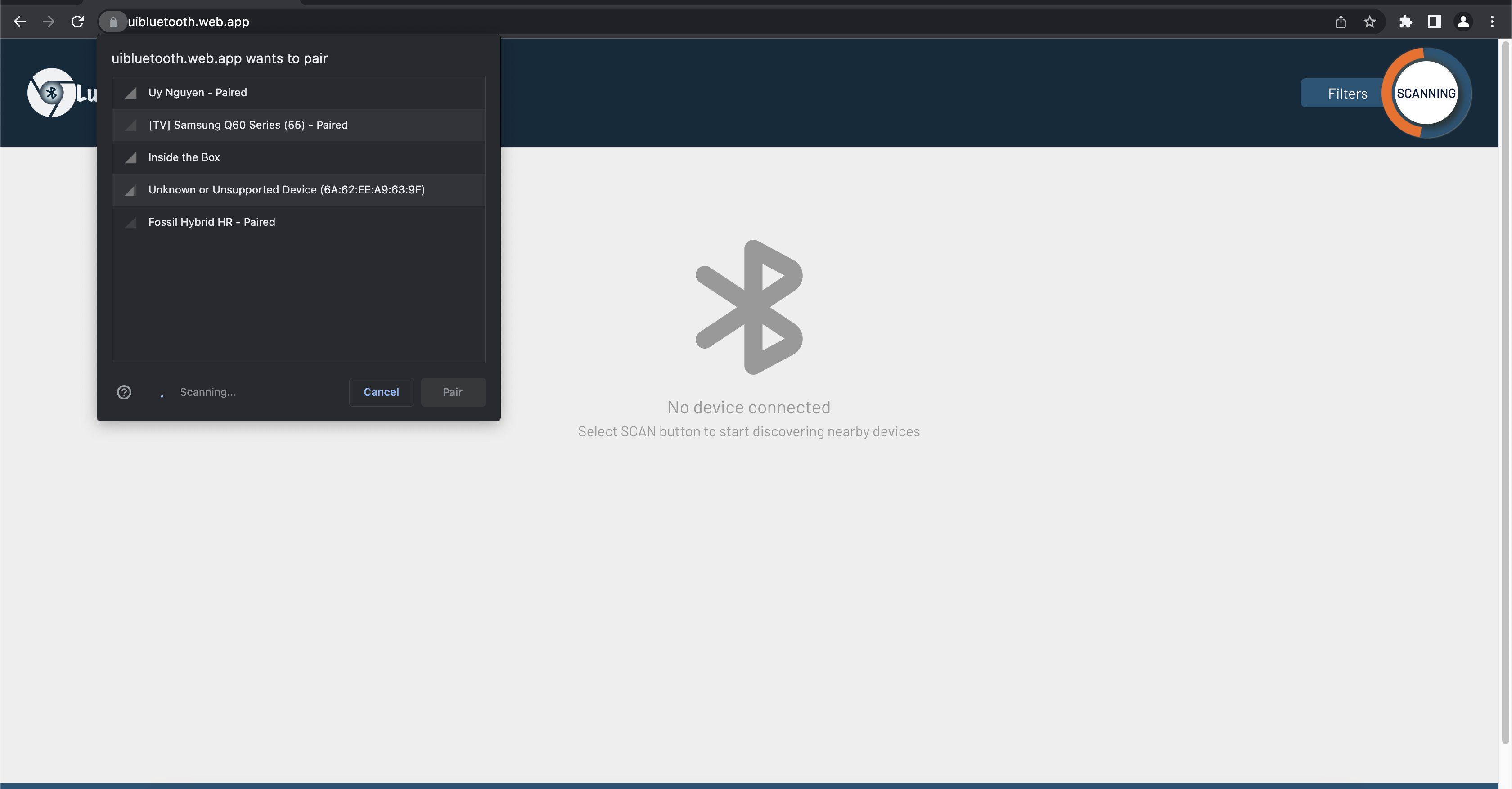
To scan for specified devices with predefined uuid, select Filters and enter your service uuid to the filter box.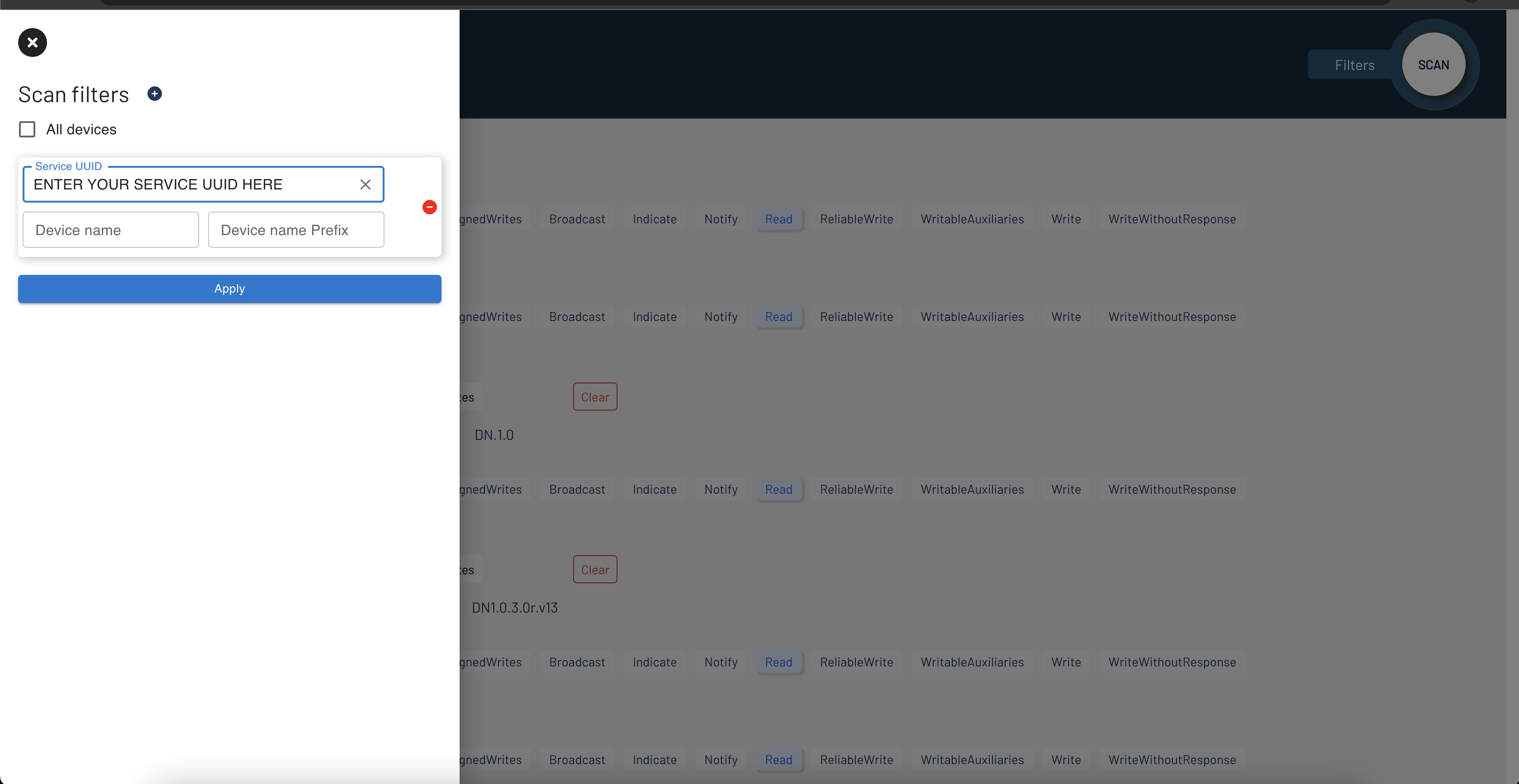
Here is the UI after the connection has been established successfully.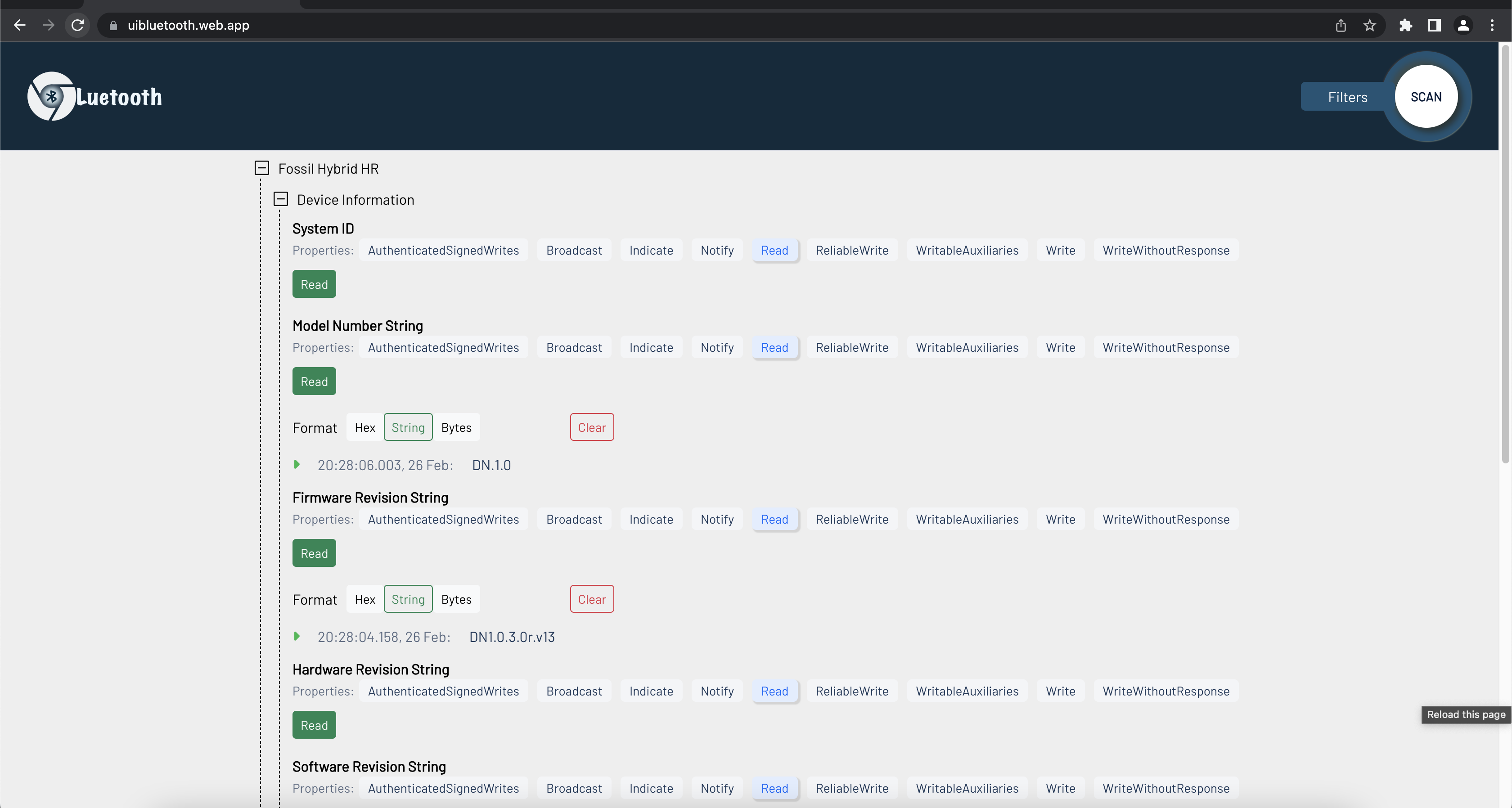
More samples
You can find more examples and ideas via this video
WebBluetooth demos for Bluetooth.rocks from Niels Leenheer on Vimeo.
Limitations
- For security purposes, we can not automatically scan and connect to a specified device. The user decides whether the web app is allowed to connect, and to which device it is allowed to connect.
- HTTPS Connection: Web Bluetooth requires a secure HTTPS connection to function properly. This means that the web application must be hosted on a secure server with a valid SSL certificate. If the application is not hosted on a secure server, the user will not be able to connect to Bluetooth devices.
- Platforms: Web Bluetooth is supported in Chrome on desktop and mobile (Require Android 6+, does not support iOS), Opera, and some versions of Microsoft Edge. It’s important to note that Web Bluetooth may not work in older or outdated browsers.
- Customization: Unfortunately, it’s not possible to customize the scan dialog of Web Bluetooth to show additional information beyond the default options. The Web Bluetooth API is designed to provide a simple and consistent interface for developers, and the scan dialog is intentionally kept simple to maintain this simplicity.
- Performance: It’s widely recognized that the stability of Bluetooth connections on native Android apps is often not as reliable as on iOS, and can be affected by factors such as the phone model, manufacturer, and version of Android being used. As a result, it’s important to note that Web Bluetooth does not function as well as native apps, especially on Android devices.
Tips & best practices
Here are some tips and best practices for optimizing the performance of Web Bluetooth applications:
- Minimize data transfers: Bluetooth communication is slow compared to other communication channels. Therefore, it’s important to minimize the amount of data that your application sends and receives over Bluetooth. For example, you can reduce the number of read and write operations and only transfer the data that is necessary for your application.
- Use notifications instead of polling: Instead of continuously polling the value of a characteristic, use notifications to receive updates when the value changes. This approach can reduce the number of read operations and improve the performance of your application.
- Disconnect when not in use: Disconnect from the GATT server when you’re not actively communicating with the device. This can reduce power consumption and improve the battery life of the device.
- Use caching: Caching can be used to store data that is frequently accessed by your application. This can reduce the number of read operations and improve the performance of your application.
- Optimize the scanning process: Scanning for devices can be a resource-intensive operation. Therefore, it’s important to optimize the scanning process by reducing the scanning time and filtering the results to only include relevant devices.
- Test your application on different devices: Test your application on different devices to ensure that it performs well across different platforms and hardware configurations.
Final thought
Despite these limitations, Web Bluetooth remains a promising technology with many potential use cases. Developers who are interested in using Web Bluetooth should carefully consider these limitations and design their applications accordingly.